Do you know who managed to cut costs by a staggering 90% by abandoning microservices for a monolith in May 2023? Not a cash-strapped startup or an indie project—Amazon itself, for its Prime Video service. The same AWS that earns billions every year by selling microservices infrastructure admitted that, sometimes, a good old monolith wins.
This reversal from the company that practically wrote the playbook on distributed systems sent shockwaves through the cloud-native community. Amazon later removed the original blog post, but the internet never forgets, as you’ll see later.
I’ve been speaking up against unnecessary or premature use of microservices architecture for five, six years now. After Amazon Prime Video went back to a monolith, I came across several eminent architects who are also speaking against microservices as default.
And yet in most tech circles, microservices are still viewed as the only way to build modern software. They dominate conferences, blogs, and job listings. Teams adopt them not because their requirements justify it, but because it feels like the obvious (and résumé-boosting) choice. “Cloud-native” has become synonymous with “microservices-by-default”, as if other approaches are as obsolete as floppy disks.
Microservices do solve real problems, but at a massive scale. Most teams don’t actually operate at that scale.
With this article, I urge you to reflect on the question the industry has mostly stopped asking: Should microservices be the default choice for building at scale? We’ll look at reversal stories and insights from seasoned architects, and weigh the trade-offs and alternatives. After considering all of this, you can decide whether your problem really needs a constellation of microservices.
Microservices: The Agility-Complexity Trade-Off
On paper, microservices look impressive. Instead of one big monolith, you split your application into many small services. Each one can be written in any language, owned by a small team, and deployed on its own schedule. If you need more capacity, you can scale only the part that’s under load. The promise is elegant: independent deployability, autonomous teams, multi-language stacks, and elastic scaling.
But the catch is that every split creates a seam, and every seam is a potential failure point. Inside a monolith, function calls are instant and predictable. Across services, those same calls become network requests: slower, failure-prone, sometimes returning inconsistent data. With dozens (or hundreds) of services, you need version management, schema evolution, distributed transactions, tracing, centralized logging, and heavy-duty CI/CD pipelines just to keep things running.
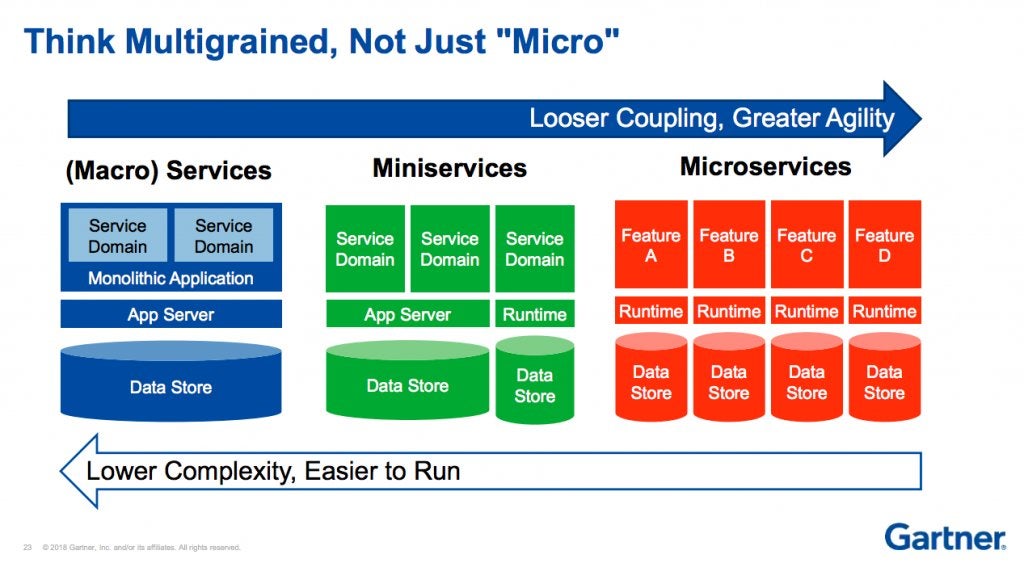
This Gartner diagram captures the trade-off perfectly: microservices exchange the simplicity of one codebase for the complexity of many.
At a massive scale (think Netflix), that trade-off may be worth it. But when operational benefits don’t outweigh the costs, teams end up paying a steep price in debugging, coordination, and glue code just to hold their product together.
Microservices make sense in very specific scenarios where distinct business capabilities need independent scaling and deployment. For example, payment processing (security-critical, rarely updated) differs fundamentally from recommendation engine (memory-intensive, constantly A/B tested). These components have different scaling patterns, deployment cycles, and risk profiles, which justify separate services.
The success of microservices hinges on clear business domain boundaries that match your team structure, as Conway’s Law predicts. If your organization naturally splits into autonomous teams that own distinct capabilities, microservices might work. (So, most “one-and-a-half pizza” startups don’t qualify, do they?)
That’s why microservices work effectively for companies like Amazon and Uber—although not always.
In fact, most organizations lack the prerequisites: dedicated service ownership, mature CI/CD, robust monitoring, and crucially, scale that justifies the operational overhead. Startups that adapt microservices prematurely often regret their decision.
So ask yourself:
Are you using microservices to solve an independent scaling problem, or are you inviting more complexity than your solution needs?
The Great Microservices Reversal
Ironically, even though tech giants are the ones that are most likely to benefit from microservices, many of these very same companies are walking back their microservices architectures, and the results are eye-opening.
Amazon Prime Video: 90% Cost Reduction with a Monolith
In May 2023, Amazon engineers admitted the unthinkable: Prime Video had abandoned microservices for a monolith. Their Video Quality Analysis (VQA) team had built what looked like a textbook distributed system: AWS Step Functions and Lambda monitored thousands of video streams through independent, scalable components. On paper, it was serverless perfection.
In practice, it was a disaster. “We realized that distributed approach wasn’t bringing a lot of benefits in our specific use case,” said Marcin Kolny in the now-archived Prime Video Engineering blog. Their “infinitely scalable” system crumbled at just 5% of expected load due to orchestration overhead.
The fix was embarrassingly simple: collapse everything into a single process. It resulted in 90% lower costs and faster performance.
Twilio Segment: From 140 Services to One Fast Monolith
Back in 2018, Twilio Segment, a customer data platform, documented a similar reversal in their brutally honest post “Goodbye Microservices”.
Their system had sprawled into 140+ services, creating operational chaos. At one point, three full-time engineers spent most of their time firefighting instead of building. As they admitted, “Instead of enabling us to move faster, the small team found themselves mired in exploding complexity. Essential benefits of this architecture became burdens. As our velocity plummeted, our defect rate exploded.”
Their solution was radical but effective: collapse all 140+ services into a single monolith. The impact was immediate. Test suites that once took an hour now finished in milliseconds. Developer productivity soared: they shipped 46 improvements to shared libraries in a year, up from 32 in the microservices era.
Shopify: Sanity over Hype
Shopify runs one of the largest Ruby on Rails codebases in the world (2.8M+ lines). Instead of chasing microservices, they deliberately chose a modular monolith: a single codebase with clear component boundaries.
Shopify’s engineers concluded that “microservices would bring their own set of challenges”, so they chose modularity without the operational overhead.
All these examples beg the question:
If even the pioneers of microservices are retreating, why are we still treating it as gospel?
Expert Voices against Microservices Mania
Some of the most respected voices in software architecture—people behind many of the systems we all admire—are also cautioning against microservices and repeating mistakes they’ve seen play out at scale. (After all, cheerleaders don’t play the game; cloud DevRels rarely build at scale.)
Rails Creator: Simplicity over Sophistication
David Heinemeier Hansson (DHH), the creator of Ruby on Rails, has long advocated simplicity over architectural trends. His analysis of the Amazon Prime Video reversal puts it bluntly:
“The real-world results of all this theory are finally in, and it’s clear that in practice, microservices pose perhaps the biggest siren song for needlessly complicating your system.”
DHH’s image of a siren song is apt: microservices promise elegance but leave teams wrecked on the rocks of complexity.
Microservices: Mistake of The Decade?
Jason Warner, former CTO of GitHub, doesn’t mince words while commenting on microservices:
“I’m convinced that one of the biggest architectural mistakes of the past decade was going full microservice.”
Warner understands scale: GitHub runs at internet scale, and he’s led engineering at Heroku and Canonical. His critique cuts deeper because it’s lived experience, beyond theoretical advice:
“90% of all companies in the world could probably just be a monolith running against a primary db cluster with db backups, some caches and proxies and be done with it.”
GraphQL Co-Creator: “Don’t”
Then there’s Nick Schrock, co-creator of GraphQL. If anyone had a reason to cheer for distributed systems, it’d be him. Instead, he says:
“Microservices are such a fundamentally and catastrophically bad idea that there are going to be an entire cohort of multi-billion companies built that do nothing but contain the damage that they have wrought.”
He goes on to describe microservices as organizational gambles:
“[Y]ou end up with these services that you have to maintain forever that match the org structure and the product requirements from five years ago. Today, they don’t make a lot of sense.”
The person who literally built tools to fix distributed system pain says don’t distribute unless you must, maybe it’s time to listen.
Other Voices Questioning Microservice Maximalism
Other engineering leaders are also reconsidering microservice maximalism.
At Uber, Gergely Orosz admitted:
“We’re moving many of our microservices to macroservices (well-sized services). Exactly b/c testing and maintaining thousands of microservices is not only hard – it can cause more trouble long-term than it solves the short-term.”
Uber still runs microservices where they’re justified, but they’re choosing their battles.
Kelsey Hightower, known for his work with Kubernetes and Google Cloud, cut through the microservices hype with CS101:
“I’m willing to wager a monolith will outperform every microservice architecture. Just do the math on the network latency between each service and the amount of serialization and deserialization of each request.”
He subsequently deleted this tweet, but the network math still grades microservices.
When pioneers like these, including those who actually solved distributed systems at scale, start waving red flags, it’s worth taking note.
My question here is:
If GitHub’s CTO thinks 90% of companies don’t need microservices, are you sure yours is part of the 10%?
The Hidden Costs of Microservices
Microservices demand such caution because of these hidden costs that teams often underestimate.
Operational Costs
A monolith is simple: in-process function calls.
Microservices replace that with networks. Every request now travels across machines, through load balancers, service meshes, and authentication layers, creating more failure points and infrastructure needs. You suddenly need service discovery (how services find each other), distributed tracing (tracking requests across services), centralized logging (aggregating logs from multiple services), and monitoring systems that understand service topology.
Each of these is necessary, but together they’re complex and expensive. Duplicated data requires extra storage. Constant service-to-service calls rack up network egress fees. Cloud costs scale faster than the apps they host. Prime Video’s workflow spent more on orchestrating S3 data transfers between services than on actual processing.
Developer Productivity Drain
In microservices, the hard part isn’t writing code; it’s navigating distributed system interactions.
In “The macro problem with microservices“, Stack Overflow identifies a critical productivity drain: distributed state forces developers to write defensive code that constantly checks for partial failures.
In a monolith, a developer can follow a code path end-to-end within one repo. In microservices, one feature might span four or five repos with different dependencies and deploy cycles. Adding a single field triggers weeks of coordination: you need to update one service, then wait for consumers to adopt, version your APIs, manage rollouts, and so on. Different teams will also typically maintain different microservices using different tech stacks, so there’s a risk that they unintentionally break something as well. Breaking changes that a compiler would catch in a monolith now surface as runtime errors in production.
Testing and Deployment Complexity
Monolith integration and end-to-end tests are faster because they run locally, in memory. Distributed systems don’t allow that luxury: real confidence requires integration and end-to-end tests across numerous service boundaries. So these tests are slower, more brittle, and require staging environments that resemble production, all of which effectively double infrastructure costs and slow feedback loops.
Many teams discover this only after their test suite becomes a bottleneck. Deployment orchestration adds another layer. Rolling updates across interdependent services require careful sequencing to avoid breaking contracts. Version incompatibility disturbs frequently: Service A works with Service B v2.1 but breaks with v2.2.
Failed deployments leave systems partially updated and difficult to recover.
Data Management and Consistency
The most underestimated complexity of microservices lies in data consistency across service boundaries.
Monoliths benefit from ACID transactions: operations complete entirely or fail entirely. Microservices split that across services, forcing you to build distributed saga (multi-step workflows with rollback logic), live with eventual consistency (data only becomes correct after a delay), or write compensation logic (extra code to undo partial failures). What was once a single database transaction now spans network hops, retries, and partial failures. Debugging inconsistent orders or payments gets much harder when state is duplicated across services.
As research confirms, data duplication, correctness challenges, and transactional complexity are the top pain points in microservice systems.
The Compounding Effect
These complexities multiply. Operational overhead makes debugging harder, which slows testing, which makes deployments riskier, which creates more incidents. Microservices don’t just shift complexity from code to operations; they tax every part of your engineering process.
Unless your scale demands it, that tax often outweighs the benefits.
Think about it:
If every network hop adds complexity and cost, does your use case really justify the price?
Beyond Microservices: Smarter Architectural Alternatives
Before defaulting to microservices, it’s worth considering how simpler, well-structured architectures can deliver comparable scalability without the distributed complexity tax. Two noteworthy alternatives are modular monoliths and service-oriented architectures.
Modular Monoliths: Structure without Distribution
Unlike traditional monoliths that become tangled messes, modular monoliths enforce strict internal boundaries through clear module APIs and disciplined separation. Each module exposes well-defined interfaces, enabling teams to work independently while deploying a single, coherent system.
As Kent Beck explains in “Monolith -> Services: Theory & Practice”, modular monoliths manage coupling through organizational discipline rather than distributed networks. The key difference: modules still communicate via explicit contracts like microservices, but they use fast, reliable function calls instead of HTTP requests that are vulnerable to network latency and partial failures.
Why does it work?
Simpler operations: microservices-level organization with monolithic simplicity
Stronger consistency: full ACID transactions
Easier debugging: one traceable system, no hunting for bugs in the ELK haystack
Better performance: function calls beat network hops
Here’s some real-world proof: Shopify’s 2.8 million-line codebase handles 30TB per minute with separate teams owning distinct modules, yet everything deploys together. Facebook runs similarly. (And principal architect Keith Adams jokes that if you want to be talked out of microservices, he’s your guy.)
With recent developments in frameworks like Spring Modulith, Django, Laravel, and Rails (as seen at scale with Shopify), modular monoliths are poised to gain wider traction in the years ahead.
Service-Oriented Architecture: The Middle Ground
Service-oriented architecture (SOA) sits between monoliths and microservices, favoring larger, domain-driven services instead of dozens or hundreds of tiny ones. These services often communicate via an enterprise service bus (ESB), which reduces orchestration overhead while preserving separation of concerns.
Instead of splitting authentication, user preferences, and notifications into separate microservices, SOA might combine them into a single “User Service”, simplifying coordination while preserving autonomy and targeted scaling. SOA provides enterprise-grade modularity without ultra-fine-grained distribution overhead.
Here’s why it works:
Right-sized boundaries: fewer, domain-aligned services instead of sprawl
Targeted scalability: scale services tied to real business domains
Pragmatic complexity: avoids ultra-fine-grained overhead while retaining modular reasoning
SOA has also been proven to work at scale. Norwegian Air Shuttle, Europe’s 9th-largest airline, used SOA to boost agility across complex flight operations. Credit Suisse’s SOA rollout powered millions of service calls per day back in the early 2000s.
Choosing Wisely: Fit over Hype
The problem you’re solving should justify your architecture.
I often use this analogy in consulting: You don’t need a sword to cut a lemon—a knife suffices. And as timeless wisdom reminds us, simplicity is the ultimate sophistication.
In all likelihood, you’re not Google (you don’t need Google-level fault tolerance), or Amazon (you don’t need massive write availability), or LinkedIn (you don’t handle billions of events a day). Most applications don’t operate at that scale, demanding fundamentally different solutions than ultra-distributed architectures.
For most systems, well-structured modular monoliths (for most common applications, including startups) or SOA (enterprises) deliver comparable scalability and resilience as microservices, without the distributed complexity tax. Alternatively, you may also consider well-sized services (macroservices, or what Gartner proposed as miniservices) instead of tons of microservices.
It’s worth asking:
If simpler architectures can deliver comparable scalability, why are you choosing the complexity of microservices?
Docker: Built for Any Architecture
Docker isn’t just for microservices—it works great across all kinds of architectures like monoliths, SOA, APIs, and event-driven systems. The real benefit is that Docker gives you consistent performance, easier deployment, and flexibility to scale up your apps no matter what architectural approach you’re using.
Docker packages applications cleanly, keeps environments consistent from laptop to production, simplifies dependency management, and isolates applications from the host system. A Dockerized monolith offers all these benefits, minus the orchestration overhead of microservices.
Microsoft’s guidance on containerizing monoliths clarifies that scaling containers is “far faster and easier than deploying additional VMs”, whether you run one service or fifty. Twilio Segment observed that containerized monoliths can “horizontally scale your environment easily by spinning up more containers and shutting them down when demand subsides.” For many applications, scaling the whole app is exactly what’s needed.
As for DevOps, a monolith in Docker is lighter to operate than a full-blown microservices setup. Logging aggregation becomes simpler when you’re collecting from identical containers rather than disparate services with different formats. Monitoring and debugging remain centralized, and troubleshooting avoids tracing requests across service boundaries.
So, it’s definitely worth considering:
Even without the complexity of microservices, Docker gives you the same advantages — clean deployments, easy scaling, and consistent environments. So why not keep it?
Wrapping Up
A few years ago, my then-8-year-old wanted a bicycle. He’d mostly ride around our apartment complex, maybe venture into the nearby lane. He didn’t need 21 gears, but those shiny shifters had him smitten—imagine riding faster by changing those gears! He absolutely wanted that mechanically complex beauty. (It’s hard to argue with a starry-eyed kid… or a founder :P).
Once he started riding the new bike, the gears slipped, the chain jammed, and the bicycle spent more time broken than on the road. Eventually, we had to dump it.
I wasn’t able to convince him back then that a simpler bicycle could’ve served him better, but maybe this article will convince a few grown-ups making architectural decisions.
We techies love indulging in complex systems. (Check: were you already thinking, What’s complex about bicycles with gears??) But the more moving parts you add, the more often they break. Complexity often creates more problems than it solves.
The point I’m making isn’t to dump microservices entirely—it’s to pick an architecture that fits your actual needs, not what the cloud giant is pushing (while quietly rolling back their own commit). Most likely, modular monoliths or well-designed SOA will serve your needs better and make your team more productive.
So here’s the million-dollar question:
Will you design for cloud-native hype or for your own business requirements?
Do you really need microservices?
Quelle: https://blog.docker.com/feed/